Communication Processes BBS 2nd Year
Communication Processes
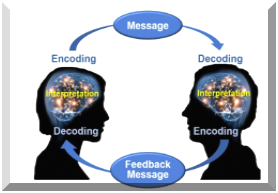
The communication process refers to the steps or stages involved in transferring information from a sender to a receiver. It is a complex and dynamic process that involves the exchange of messages through various channels. According to Jonathan Scott, ‘Communication is about sending, receiving, and understanding information and meaning’. It involves several components such as the sender of the communication, the actual message being sent, the encoding of
a. Developing an idea: The beginning of the communication
process involves the sender creating an idea that they plan to send to another
person or group of people. Essentially, they're planning the overall subject
matter or information they want to transmit.
b. Encoding the message: Once the sender develops an idea,
they translate it into a form that can be transmitted to someone else. This
means they transform the thoughts of the information they want to send into a
certain format. For example, if you are writing a letter, you'll translate your
idea into words. The message can also be nonverbal, oral, or symbolic.
c. Selecting the channel of
communication:
Next, the sender decides how the message will be sent. This involves selecting
the most suitable medium for the message they're relaying. Some communication
mediums include speaking, writing, electronic transmission, or nonverbal
communication. If you're communicating at work, make sure to select the proper
and most professional channel of communication.
d. Transmitting the Message: After the medium is chosen, the
message then begins the process of transmission. The exact process of this will
depend on the selected medium. For the message to be properly sent, the sender
should have selected the appropriate medium.
e. Receiving the message: Next, the message is received by
the recipient. This step in the communication process is done by hearing the
message, seeing it, feeling it, or another form of reception.
f.
Decoding
the message: The
receiver then decodes the sender's message. In other words, he interprets it
and converts it into a thought. After he’s done this, he analyzes the message
and attempts to understand it. The communication process is performed
effectively when the sender and receiver have the same meaning for the
transmitted message.
g. Providing feedback: Lastly, unless it's a one-way
communication, the receiver will provide feedback in the form of a reply to the
original sender of the message. Feedback provides the recipient with the
ability to ensure the sender that their message was properly received and
interpreted. Between two people, this is two-way communication.
Elements of Communications
The
elements of communication are the essential components that constitute the
process of transmitting information from a sender to a receiver. The key
elements include:
a.
Sender: This is the
person or entity initiating the communication. The sender encodes a message,
which could be in the form of thoughts, ideas, feelings, or information.
b. Message: The message is the information or content that the sender wishes to convey. It could be verbal, written, non-verbal, or symbolic.
c.
Encoding: Encoding is the
process of converting the sender's message into a symbolic form, such as words,
gestures, or signals, that can be understood by the receiver.
d.
Channel: The channel is
the medium through which the encoded message is transmitted from the sender to
the receiver. Channels can include face-to-face communication, written
communication, telephone, email, or other forms of media.
e.
Decoding: Decoding is the
process by which the receiver interprets and understands the message sent by
the sender. It involves translating the encoded message back into its original
form.
f.
Receiver: The receiver is
the individual or group for whom the message is intended. Receivers play a
crucial role in the communication process by interpreting and responding to the
message.
g.
Feedback: Feedback is the
response or reaction provided by the receiver. It helps the sender to gauge the
effectiveness of the communication and whether the message was understood as
intended.
h.
Noise: Noise refers to
any interference or distortion that can disrupt the communication process. It
can be external (such as background noise) or internal (such as distractions or
biases).
i.
Context: The context
encompasses the situational factors, social and cultural elements, and the
environment in which the communication takes place. It significantly influences
how the message is interpreted.
j.
Feedback Loop: The
ongoing cycle of communication, where feedback from the receiver can lead to
further adjustments or clarification in the message, ensuring a more effective
exchange of information.
Effective
communication occurs when the sender's message is accurately decoded by the
receiver, leading to shared understanding. However, various factors, such as
language barriers, cultural differences, and environmental distractions, can
impact the communication process and contribute to misunderstandings.







Post a Comment